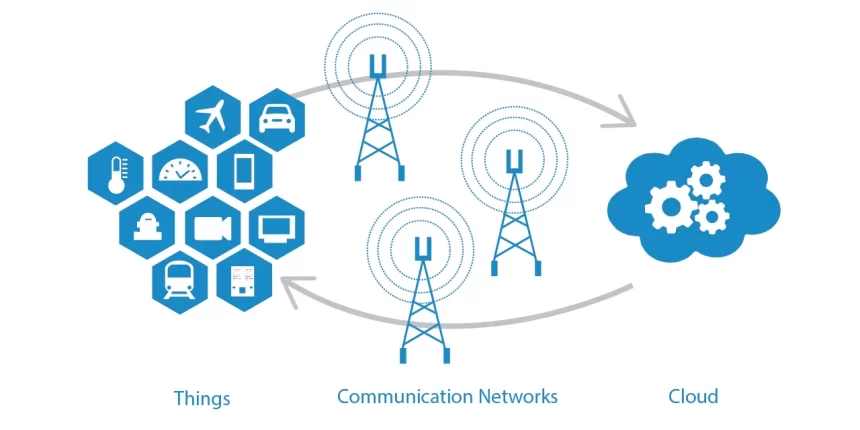
Edge computing is a networking theory that seeks to bring computation close to the data source as possible to reduce latency and bandwidth utilization. Simply put, it implies running fewer cloud processes and transferring those processes to local locations like on a user’s computer. Bringing computing to the edge of the network minimizes the amount of long-distance contact between a client and a server that may take place. So, let’s discuss what is edge computing, its benefits, drawbacks, and types.
What is edge computing, and why is it essential?
- Privacy: Avoid submitting all the raw data to cloud servers to be stored and analyzed.
- Real-time Responsiveness: Response time may often be a crucial factor.
- Reliability: Even when disconnected to cloud servers, the system is capable of operating. Removes a single failure point.
- It also decreases latency, reduces bandwidth use, and associated cost and also decreases server resources and related cost.
- Added functionality
Drawbacks
So, till now, we have discussed what is edge computing? Let’s look into the drawbacks and future, and use cases.
One disadvantage is that it can raise attack vectors. With the addition of more smart devices into the mix, there are new opportunities for malicious actors to compromise them.
Another drawback is the fact that more local hardware is needed. But hardware’s dropping costs make it easier to build smarter devices. One way to diminish the need for additional hardware is to use edge servers to the full.
Forms of Edge Computing
- Device Edge: In the existing environments,it is taken to the customers in this model. For example, Greengrass AWS, and IoT Edge Microsoft Azure.
- Cloud Edge: This model is essentially an extension of the public cloud. Content Delivery Networks are examples of this topology where static information is stored and distributed across geographically spread edge locations.
[Also read:Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing]
Examples
- Drones: Drones can touch remote locations that human beings can’t even dream of. It helps these drones to real-time monitor, analyze and respond to the analysis.
- Augmented Reality: Augmented Reality took a step further with the launch of edge computing. The platforms can provide highly localized data aimed at the user’s point of interest, thereby improving the AR services.
- Automated Vehicles: Self-driving vehicles are coming up from companies like Google and Uber. It has a crucial role to play in designing these automated vehicles. Such vehicles may use this to process and relay critical data in real-time to nearby commuting vehicles.
[Read also:Advancement in Adoption of Drones Technology]
Future of Edge Computing
It has an advantage over the current network in some cases. Self-driving cars would operate quickly if they weren’t going back and ask the cloud every time they need to make a decision. Likewise, to minimize latency, Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality often require the need for edge processing.
[Read also:How Ai and computer technologies are Improving autonomous cars]
Other edge computing use cases include Industrial Automation, Retail, Video Surveillance, and Smart Homes & Offices. According to MarketsandMarkets, the retail market expects to be the fastest-growing segment of edge computing. IoT is set to be valued at $7.5T by 2025, according to estimates from McKinsey & Co.
Conclusion
We believe that next-gen computing will be profoundly affected by Edge Computing. And will continue to explore new uses that the Edge will make possible.