Business management shapes how companies plan, organize, and lead their teams toward clear goals. It connects strategic vision with daily execution, ensuring every resource – from people to capital – is used effectively.
Strong management drives efficiency, innovation, and steady growth.
So, in this guide, we’ll explain what business management means, how its core functions work, and which management styles help organizations perform at their best.
What Is Business Management?
Business management involves planning, organizing, and directing a company’s resources to achieve defined business objectives. It connects strategic planning with daily operations to help an organization meet organizational objectives efficiently.
A business manager coordinates financial management, human resources, and operations management to maintain productivity and drive organizational success. Business administration, which is closely related to management, focuses on processes and decision-making that guide company growth.
We can outline four key areas:
- Allocating resources effectively to meet goals
- Coordinating teams and workflows
- Monitoring business processes and performance
- Supporting leadership roles and strategic decision making
Core Functions of Business Management
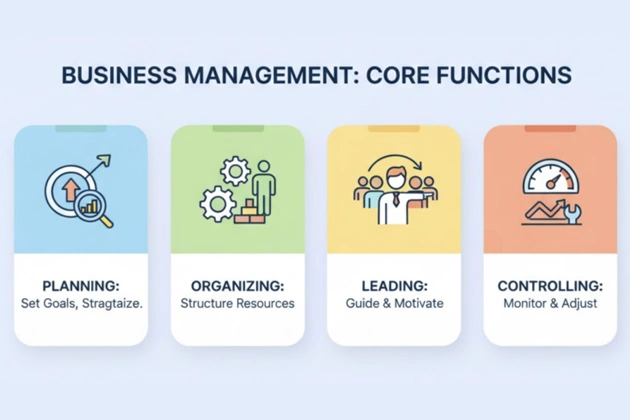
Business management focuses on four core functions: planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. These elements form the foundation of every business management system and guide how a company operates from strategy to execution.
Each function contributes to achieving business objectives and maintaining effective business management across departments.
Let’s break them down.
Planning
Planning defines goals and outlines how to reach them. It involves strategic planning, financial analysis, and identifying business strategies that guide long-term growth. A business manager uses data, market research, and project management tools to forecast trends and align operations with the company’s goals.
Organizing
Organizing structures the company’s resources – human resources, materials, and finances – to improve efficiency. Operations managers allocate resources and design business processes that help teams perform effectively. This function connects leadership roles and operational processes within departments.In sectors driven by technology and product innovation, operations managers often collaborate with leading hardware design companies such as Intechhouse, to align manufacturing, engineering, and business objectives. Partnerships like these help synchronize design efficiency with strategic management goals.
Leading
Leading focuses on motivating and guiding people. Strong leadership skills and effective communication improve employee performance and customer satisfaction. A human resources manager plays a vital part in developing leadership roles and maintaining a positive work environment that supports the organization’s workforce.
Controlling
Controlling evaluates performance, monitors progress, and compares results with set objectives. Managers use measurable indicators to track business activities and support continuous improvement. Effective management depends on feedback and problem solving to adjust strategies and sustain company growth. Many organizations now rely on customer analytics software to gather real-time insights into buyer behavior and market trends. Tools like these transform raw data into actionable metrics, helping managers refine strategies and improve business performance.
Main Roles in Business Management
Want to start a career in business management but don’t know which path to take?
We’ve got you covered.
Business management includes several specialized positions that handle specific functions across an organization.
Each role supports the company’s goals through leadership, coordination, and performance tracking. In short:
- Strategic Manager — focuses on vision and market direction.
- Operations Manager — ensures smooth workflows and logistics.
- Financial Manager — manages budgeting and performance metrics.
- Marketing Manager — drives visibility and customer acquisition.
- HR Manager — develops and retains talent.
- Risk Manager — mitigates potential disruptions.
Now, let’s compare the main roles that define how a business operates.
| Position | Main responsibilities | Annual salary (US) | Key skills and focus areas |
| Strategic Manager | Develops long-term business strategies, evaluates market trends, and leads strategic decision making. | $95,000-$150,000 | Strategic management, problem solving, financial analysis, strategic planning |
| Operations Manager | Manages day to day operations, optimizes workflows, and coordinates operational processes. | $75,000-$120,000 | Operations management, project management, continuous improvement |
| Financial Manager | Oversees budgeting, forecasting, and financial procedures to support business growth. | $90,000-$140,000 | Financial management, financial analysis, decision making skills |
| Marketing Manager | Designs marketing strategies, leads brand management, and monitors customer satisfaction. | $80,000-$130,000 | Marketing strategy, effective marketing management, workplace communication |
| HR Manager | Handles recruitment, training, and employee performance to maintain a positive work environment. | $70,000-$115,000 | Human resources, leadership skills, employee relations |
| Risk Manager | Identifies potential risks, creates prevention plans, and supports strategic decisions for stability. | $85,000-$130,000 | Risk assessment, strategic decision making, financial management |
Management Styles in Business
Management style describes how a business manager directs people, makes decisions, and manages day to day operations.
We can define four of them.
The way leaders communicate and delegate tasks shapes productivity, motivation, and overall business performance. So, each management style offers different benefits depending on company goals and culture.
- Democratic Management Style. Involves employees in decision making and values open feedback. It helps create engagement and a positive work environment built on collaboration.
- Autocratic Management Style. Centralizes authority with the manager, which allows quick decisions and consistent direction in high-pressure or time-sensitive situations.
- Paternalistic Management Style. Balances authority with care for employee development and well-being, fostering loyalty and strong workplace relationships.
- Laissez-Faire Management Style. Gives experienced teams independence to make their own decisions, encouraging creativity, accountability, and innovation.
Conclusion
Business management brings structure to how companies plan, organize, and control their operations. It connects strategic goals with daily decisions, helping organizations use their resources efficiently and support long-term company growth.
Strong leadership, effective communication, and practical management skills define how teams perform and how a business meets organizational objectives.
Key takeaways:
- Business management involves planning, organizing, leading, and controlling resources to meet goals.
- Core roles such as financial management, operations management, and human resources management maintain coordination across departments.
- Management styles – democratic, autocratic, paternalistic, and laissez-faire – shape decision making and team engagement.
- Effective business management depends on adapting strategies to the company’s needs and promoting continuous improvement across business processes. To support that improvement, tools like Enji can help streamline your business and marketing management workflows, making everyday operations more efficient.